Maximizing Asset Longevity: Essential Risk Management Strategies for 20247 Risk Management Strategies in Physical Asset Management

In today’s evolving business environment and technological advancement, physical assets represent a significant investment and are crucial to operational success. From manufacturing machinery and IT infrastructure to vehicles and real estate, managing these assets efficiently is more important than ever. However, the complexity of modern operations means that the risks associated with physical assets are also growing. These risks can range from equipment failures and environmental impacts to compliance issues and operational disruptions.
Effective risk management in physical asset management is not just about avoiding problems but also about strategically positioning assets to deliver maximum value throughout their lifecycle. With the integration of advanced technologies, shifting regulatory landscapes, and heightened focus on sustainability, the traditional approaches to asset management are evolving.
In 2024, businesses are faced with new challenges and opportunities in safeguarding their physical assets. Predictive maintenance powered by IoT, advanced risk assessment techniques, and robust emergency response planning are just a few of the strategies reshaping the landscape. As organizations strive to enhance their operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and minimize costs, understanding and implementing effective risk management strategies becomes imperative.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential risk management strategies for physical asset management. It explores the latest trends and technologies, offers actionable insights, and provides data-driven recommendations to help organizations navigate the complexities of asset management. Whether you’re managing a fleet of vehicles, overseeing manufacturing equipment, or maintaining critical infrastructure, these strategies will equip you with the tools and knowledge needed to optimize asset performance, ensure safety, and achieve long-term success.
By adopting a proactive and data-driven approach to risk management, you can not only protect your physical assets but also drive operational excellence and secure a competitive edge in the market. Let’s explore the key strategies that will help you maximize asset longevity and navigate the challenges of 2024 and beyond.
Understanding Risk in Physical Asset Management
Risk in physical asset management encompasses any potential event or condition that could negatively impact the performance, safety, or lifespan of an asset. These risks can stem from various sources, including equipment failure, environmental factors, operational errors, and regulatory changes.
7 Key Risk Management Strategies
1. Predictive Maintenance and Condition Monitoring**
Predictive maintenance uses data analytics and IoT sensors to monitor the condition of assets in real time. By analyzing this data, organizations can predict when an asset is likely to fail and perform maintenance before the failure occurs.
Benefits:
- Reduced Downtime: Prevents unexpected equipment failures and associated downtime. According to McKinsey, predictive maintenance can reduce downtime by 30-50%.
- Cost Savings: Minimizes maintenance costs by performing maintenance only when necessary. The same McKinsey report indicates that predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by 10-40%.
- Extended Asset Lifespan: Maintains optimal asset performance and extends the useful life of assets.
Implementation:
- IoT Sensors: Deploy sensors to continuously monitor critical asset parameters such as temperature, vibration, and pressure.
- Data Analytics: Use advanced analytics tools to analyze sensor data and predict potential failures.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Develop a maintenance schedule based on predictive analytics insights.
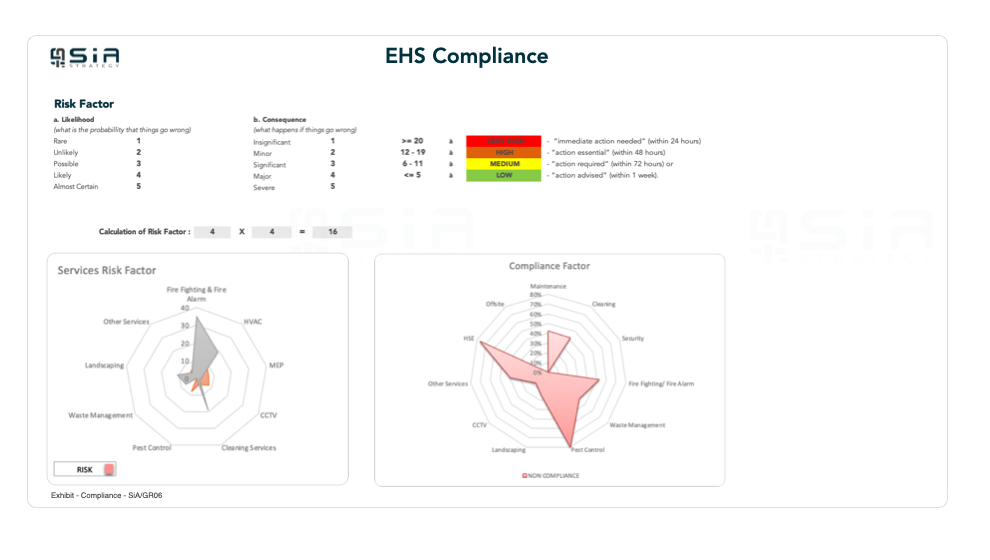
2. Risk Assessment and Prioritization
Conducting a thorough risk assessment helps identify and prioritize the risks associated with physical assets. This involves evaluating the likelihood and impact of various risk scenarios.
Steps:
- Identify Risks: List all potential risks, including equipment failures, natural disasters, and human errors.
- Assess Likelihood: Evaluate the probability of each risk occurring.
- Assess Impact: Determine the potential impact of each risk on asset performance, safety, and financial outcomes.
- Prioritize Risks: Rank risks based on their likelihood and impact to focus on the most critical ones.
3. Regular Inspections and Audits
Routine inspections and audits are essential for identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Regular checks ensure that assets are in good working condition and comply with regulatory standards.
Best Practices:
- Inspection Schedule: Develop a comprehensive schedule for regular inspections and audits.
- Checklists: Use detailed checklists to ensure all critical aspects of asset performance and safety are evaluated.
- Documentation: Keep thorough records of all inspections, findings, and corrective actions taken.
4. Training and Competency Development
Ensuring that staff are properly trained and competent is crucial for effective risk management. Well-trained employees are more likely to operate and maintain assets correctly, reducing the risk of failures and accidents.
Strategies:
- Training Programs: Implement regular training programs on asset operation, maintenance, and safety procedures.
- Certification: Encourage staff to obtain relevant certifications in asset management and maintenance.
- Knowledge Sharing: Foster a culture of continuous learning and knowledge sharing within the organization.
5. Emergency Response Planning
Having a robust emergency response plan in place is vital for managing risks associated with unexpected events such as natural disasters, equipment failures, or safety incidents.
Components:
- Emergency Procedures: Develop detailed procedures for different types of emergencies.
- Communication Plan: Establish clear communication channels for reporting and responding to emergencies.
- Training and Drills: Conduct regular training sessions and drills to ensure staff are prepared to handle emergencies effectively.

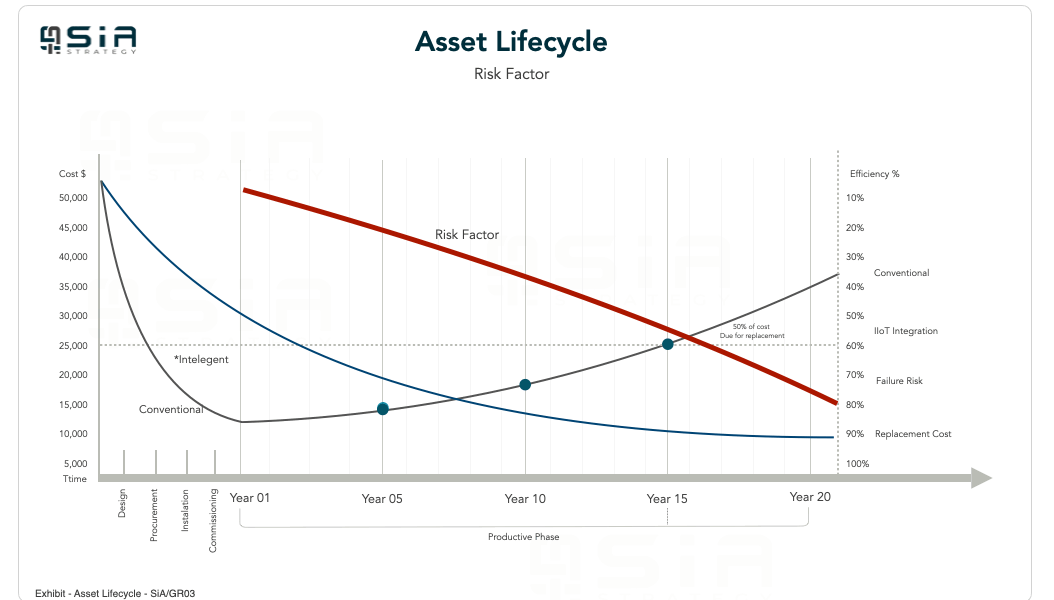
6. Asset Lifecycle Management
Effective asset lifecycle management involves planning for and managing assets from acquisition to disposal. This approach helps in anticipating and mitigating risks at each stage of the asset’s life.
Phases:
- Acquisition: Ensure that new assets meet all performance, safety, and regulatory requirements.
- Operation: Implement best practices for operating and maintaining assets to optimize performance and mitigate risks.
- Disposal: Plan for the safe and compliant disposal of assets at the end of their useful life.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with relevant regulations and standards is crucial for mitigating legal and financial risks. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal action, and reputational damage.
Actions:
- Regulatory Awareness: Stay informed about applicable regulations and industry standards.
- Compliance Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with all regulatory requirements.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of compliance-related activities and findings.
Conclusion
Effective risk management in physical asset management is essential for maintaining optimal asset performance, ensuring safety, and achieving financial goals. By implementing strategies such as predictive maintenance, regular inspections, staff training, and emergency planning, organizations can mitigate risks and enhance the value of their physical assets. As we move into 2024, adopting a proactive and data-driven approach will be key to navigating the complexities of physical asset management.
For instance, according to a report by Deloitte, companies that implement comprehensive risk management strategies can reduce their total cost of ownership (TCO) of physical assets by up to 20%. By staying informed and adaptable, organizations can not only protect their assets but also gain a competitive edge in the market.
REQUEST A CALL BACK
CHECK MORE
-
Optimizing Asset Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Best Practices and Deep Dive
Supported by a robust sales force and tight cost controls, Pharm Ltd. experienced sustained double-digit growth over a number of years, only to find that their supply chain struggled to keep pace.
October 10, 2024 -
Effective FM Contract Mobilization: A Comprehensive Guide to Seamless Transition and Execution
Supported by a robust sales force and tight cost controls, Pharm Ltd. experienced sustained double-digit growth over a number of years, only to find that their supply chain struggled to keep pace.
September 28, 2024 -
Mastering Facilities Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Management
Supported by a robust sales force and tight cost controls, Pharm Ltd. experienced sustained double-digit growth over a number of years, only to find that their supply chain struggled to keep pace.
September 28, 2024 -
Turning Setbacks into Success: 5 Traits For Every Entrepreneur to Stay Strong and Focused on the Big Picture!
Supported by a robust sales force and tight cost controls, Pharm Ltd. experienced sustained double-digit growth over a number of years, only to find that their supply chain struggled to keep pace.
September 21, 2024




